Simply put, RAN is the base station, which is the network. Before the advent of the 5G era, the base station (RAN) consisted of three parts: the antenna, the RRU (radio-frequency pull-out unit), and the BBU (baseband processing unit). RRU is used to transmit and receive signals, while BBU is used to process signaling messages.
In the era of 1G and 2G, BBU, RRU and power supply units and other equipment were placed in one cabinet, which was very bloated
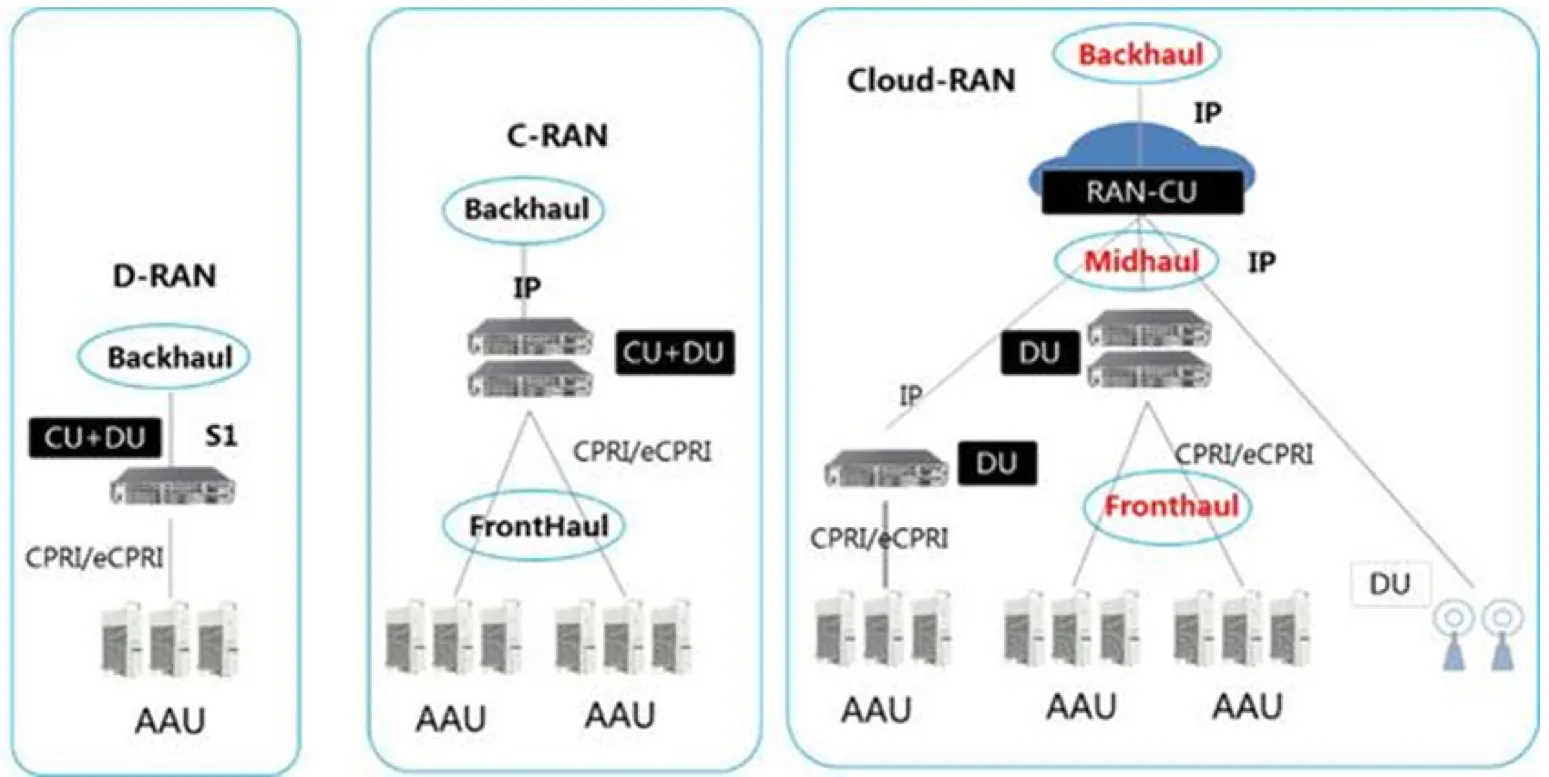
In the 3G era, distributed base stations are proposed. In other words, BBU can be separated from RRU. RRU can even be hung under the antenna, instead of being in the same cabinet with BBU. This is called D-RAN (distributed Wireless Access Network). With the development of technology (largely due to the high maintenance costs of operators), C-RAN was born.
What is C-RAN? It’s the Centralized RAN. It can also refer to the cloud-ran, which means Centralized wireless access. The separation scheme between BBU and RRU is still adopted, but RRU is infinitely close to the antenna, which greatly reduces the attenuation through the feeder (the connection between antenna and RRU). Meanwhile, BBU is migrated and concentrated in CO (central machine room) to form BBU baseband pool. And CO and RRU are connected through the prequel network. This is very conducive to inter-cell cooperation, reduce the transmission caused by attenuation, saving costs.
Overseas operators are also exploring more advanced network architectures. In 2016, overseas operators formed the X-RAN Alliance with the goal of replacing traditional hardware-based RAN with open, alternative, standardized devices. The alliance focuses on three areas: coupling the RAN control plane to the user plane, building a modular eNodeB software stack using COTS hardware, and exposing the south and North interfaces.
X-ran and C-RAN are often considered the precursors of O-RAN. The reason begins with how O-ran was born.
Wireless network construction has always been the most important part of operator network integrated cost (TCO), accounting for roughly 60% ~ 70%. Most operators have just experienced huge investment in 4G networks, and will face the pressure of investment and construction of 5G networks.
5G networks differ from 4G networks in their speed, bandwidth and frequency band, which means that 5G networks will be far less penetrating than 4G networks. To put it in layman’s terms, 4G requires only one base station to cover an area, whereas 5G requires five base stations. As a result, China will need millions, if not millions, of 5G mini-base stations in the future.
At the same time, 5G network is the network that operators must invest in, and large-scale network construction is bound to bring great cost. At this time, it is necessary to introduce new technologies and new schemes to reduce the construction difficulty and wireless network investment through scheme innovation.
In the context of slowing growth of “wireless Internet” traffic revenue and declining voice revenue, vertical industry is the “blue ocean market” that operators must enter, and expanding operators’ profitability will be the top priority of 5G networks. New business in vertical industry means more diverse business types, more complex network management, more efficient resource management solutions and more flexible network architecture to facilitate business innovation.
In this context, the operator – led O-RAN industry alliance came into being.