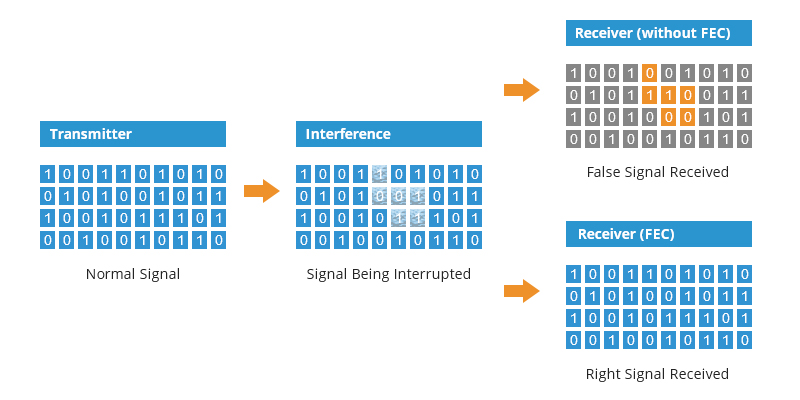
Forward error correction (FEC) is a digital signal processing technique used to enhance data reliability. It does this by introducing redundant data, called error correcting code, prior to data transmission or storage. FEC provides the receiver with the ability to correct errors without a reverse channel to request the re-transmission of data. As we know, sometimes optical signals could deteriorate due to some factors during transmission, which may lead to misjudgment at the receiver end, possibly mistaking “1” signal for “0” signal, or “0” signal for a “1” signal. If the number of errors in transmission is within the correction capacity (discontinuous errors), the channel decoder will locate and correct the false “0” or “1” to improve the quality of the signal.
The development of Forward Error Correction in optical communications can be divided into three generations. The first generation FEC represents the first to be successfully used in submarine systems and terrestrial systems. As WDM systems matured, a stronger second generation FEC was installed in commercial systems. The advent of third-generation FEC opened up new vistas for the next generation of optical communication systems.
Application of FEC in 100G Networks
What Is FEC in 100G Data Transmission? In the context of fiber-optic networking, FEC is used to address optical SNR (OSNR) - one of the key parameters that determine how far a wavelength can travel before it needs regeneration. FEC is especially important at high-speed data rates, wherein advanced modulation schemes are required to minimize dispersion and signal correspondence with the frequency grid. Without the incorporation of FEC, 100G transport would be limited to extremely short distances. To implement long-haul transmission (> 2500 km), the system gain must be further improved by approximately 2 dB. FEC‘s upgrade from hard-decision to soft-decision fills this performance gap.
As the push for ever-higher transmission rates has continued, soft-decision forward error correction (SD-FEC) schemes have grown in popularity. Although these can require a byte overhead around 20% — nearly three times as large as the original RS coding scheme — the gains they produce in the context of high-speed networking are substantial. FEC that results in a 1 to 2 dB gain on a 100G network, for instance, translates to a 20% to 40% greater reach.
HTF support DWDM Solution design, Single channel support 400G/200G/100G dwdm upgrade. 100G QSFP28 80KM optical module has price advantages to help you save cost and win more local market. welcome to contact HTF. For further information, please, Contact HTF expert sales team today! Assist you to choose suitable solution and help you to save cost. info@htfuture.com 008618123672396

