Do you know how many rates the different descriptions represent? This article will take you through it.
1. Fiber Channel: Fibre Channel Protocol
FC (Fibre Channel Protocol originated from) the American National Standards Committee was originally proposed to solve the negative impact of I/O transmission bottlenecks on the overall storage system, thus forming a cluster of Fibre Channel standard protocols, coupled with the high bandwidth, low latency, low bit error rate, flexible topology of FC networks, FC networks have been widely used in information storage, banking, telecommunications, radio, television, industrial instrumentation, and is gradually beginning to be used in aerospace, military, and industrial real-time control applications. In contrast to traditional Gigabit Ethernet, although the switched networking structure is similar to that of Ethernet, FC networks have features that traditional Ethernet does not have, such as support for a variety of upper layer protocols, support for a variety of underlying transmission media, support for credit-based traffic control, plus support for link rates above 16Gbps and support for a variety of topologies, which already gives an absolute advantage in the process of network selection.
2. CPRI: Common Public Radio Interface
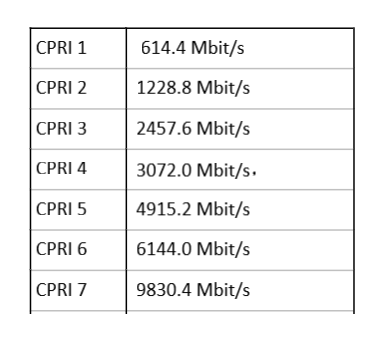
CPRI was established in 2003 by base station suppliers such as Ericsson, Nokia Siemens Networks, Alcatel-Lucent, NEC and Huawei Technologies to define a public specification to standardise the protocol interface between base station equipment (baseband units and remote radio units). So what exactly are the CPRI: 2/3/4/5/6/7 rates? Please see the table below
3. Ethernet:Ethernet transmission protocol

4. SONET (Synchronous Optical Network)
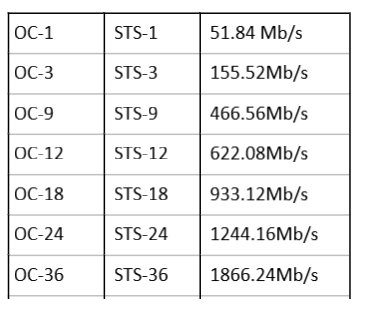

5. SDH is a synchronous
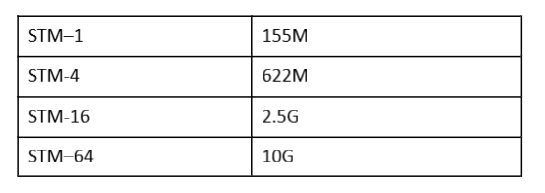
transmission system. The original PDH equipment did not have a world standard for interfaces. The interfaces were different for each production and different manufacturers could not connect directly. It was very inconvenient for user group networks and severely restricted the development of communication. sdh is a synchronous transmission system, the smallest module unit is STM-1, 155.520Mbit/s. All transmission modules defined by sdh are strictly 4 times related, there is never anything like STM-2, STM-3, STM-7 and so on, only 1, 4, 16, 64 and 256 modules.
What is the rate of STM-x on SDH equipment?