OADM (Optical Add-Drop Multiplexer) – Working Principle and Applications in WDM Systems
Working Principle
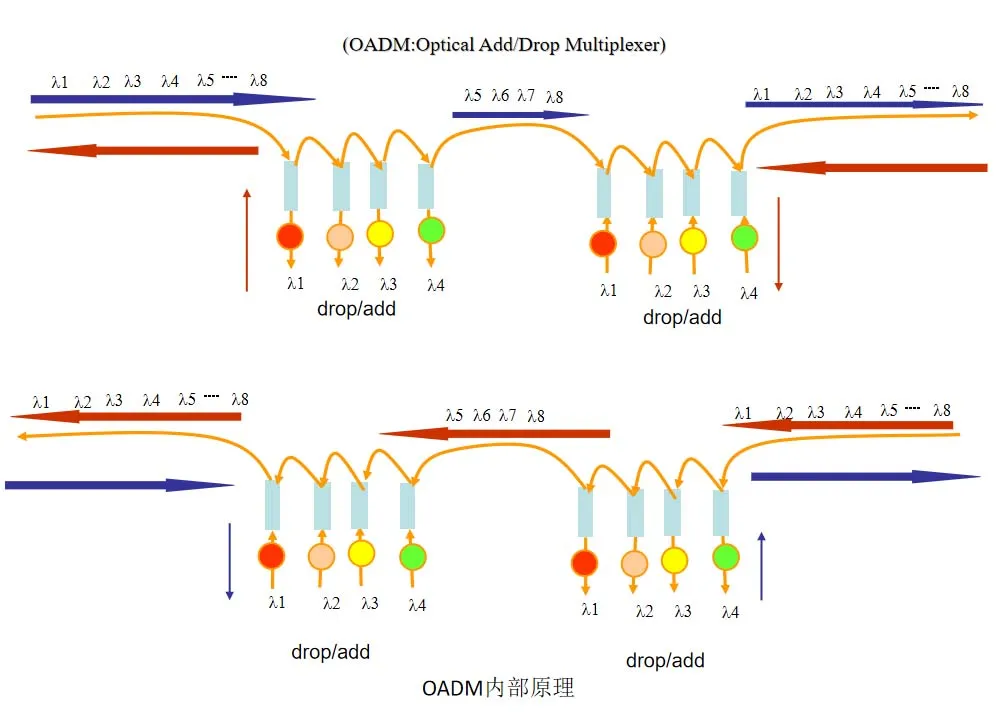
The primary function of an OADM is to perform add-drop multiplexing on WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing) optical signals. It allows the selective insertion or removal of specific wavelength signals without the need to demultiplex the entire signal. OADM uses optical filtering devices (such as AWGs or fiber Bragg gratings) to selectively add or drop certain wavelength signals.
- Input Signals: The OADM receives WDM signals from the upstream channel, which consist of multiple optical signals at different wavelengths.
- Selective Operation: Through optical filters and optical switches, the OADM selectively removes a particular wavelength signal from the input and outputs it via the “Drop” port (downstream port). Simultaneously, the OADM can insert a new wavelength signal from an external source and output it via the “Add” port (upstream port).
- Through Wavelengths: Wavelength signals that are not processed by the OADM pass through the device unaffected, continuing their transmission with minimal loss.
Application Scenarios
Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs) and Access Networks:
OADMs are ideal for scenarios requiring flexible wavelength selection and add-drop operations, especially in environments like MANs and access networks. OADMs dynamically add or drop wavelengths based on specific demands.
- Example: Wavelength Management in MANs:
In a city-wide optical fiber network, OADMs can add or remove wavelength signals based on requirements. For instance, in a multi-tier urban optical network, OADMs can connect local traffic wavelengths to the optical network without affecting communication in other areas.
Ring Network Structures:
OADMs are widely used in ring networks, effectively achieving add-drop multiplexing and reducing network complexity.
- Example: Optical Ring Networks:
OADMs are extensively deployed in ring networks to add or remove wavelength signals while ensuring uninterrupted data flow within the ring. For example, in a long-distance optical ring network, OADMs can transmit specific wavelength signals to designated nodes, enabling flexible data flow scheduling.
OADM Applications in WDM Systems
In WDM systems, OADMs allow flexible adjustment of signal routing between different nodes by inserting and removing wavelength signals. This makes them particularly suitable for medium-scale networks requiring wavelength management. For example, in metropolitan area networks, OADMs can extract specific service wavelengths for processing or forwarding while allowing other wavelength signals to continue transmission.