1. History of multi-mode fiber
Multi-mode fiber is the first practical fiber, its larger core radius and higher numerical aperture in the 1970s with LED light source formed the first generation of optical fiber communication system, applied in long-distance and short-distance communication. With the advent of single-mode fiber, multi-mode fiber is subsequently limited to short range applications due to the low cost of its overall system.
The original multimode fiber used a core diameter of 50um and a relative refractive index difference of 1%. Due to the very large spot diameter of LED, the designed multi-mode fiber could not effectively capture the LED light energy, so the 62.5um multi-mode fiber was developed. The 62.5um multi-mode fiber has a 2% relative refractive index difference, and its numerical aperture also increases. More light from LED is coupled to the multi-mode fiber. In the middle 1990s, the low-cost VCSEL laser was developed. Due to the characteristics of small light spot and numerical aperture of the VCSEL itself, the multi-mode fiber with a core diameter of 50um with 1% relative refractive index difference was pulled back to the application again, and has been widely used in short-distance optical fiber communication till now.
2. Typical design of multi-mode fiber
In order to obtain the ideal mode dispersion, the refractive index distribution of conventional multimode fiber adopts the shape of parabola or near-parabola. For bending resistant multimode fiber, the external groove design is generally adopted.
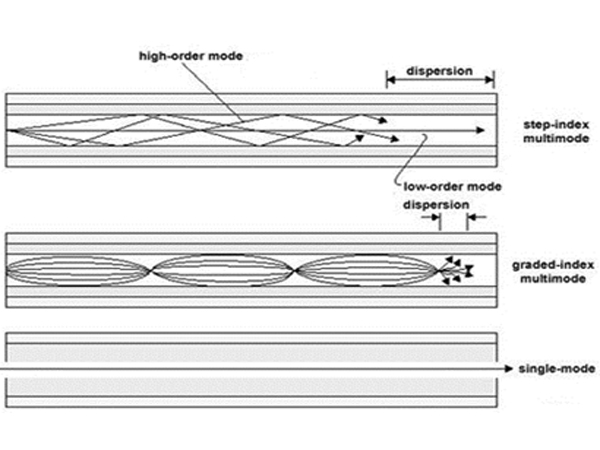
3. Factors influencing bandwidth of multimode fiber
The main factors that affect the bandwidth of multimode fiber are fiber and light source.
The factors of optical fiber mainly include material dispersion and mode dispersion.
Due to the characteristics of the multimode fiber itself, there are up to 19 mode groups that can be transmitted in the multimode fiber, and the dispersion between the modes can be very large if not precisely controlled. If VCSEL is used, mode dispersion is generally reflected by EMB of effective mode bandwidth; if LED is used, it is represented by OFL BW of full injected bandwidth.
The effective mode bandwidth and material dispersion of the fiber can be obtained from the fiber specification of the fiber manufacturer. The degree of influence on the bandwidth, the mode bandwidth and the material dispersion do not have absolute size, depends on the light source. Generally speaking, LED light source and material dispersion are the main limiting factors of link bandwidth. For VCSEL, the current mode bandwidth is the main limiting factor of link bandwidth.
Factors from the light source VCSEL can be referenced to its ring flux EF (Encircled flux). The definition of VCSEL‘s Encircled flux is as follows. It is the integral of normalized light power along the core radius, which represents the distribution of light power among each mode in the core.
The distribution of its EF should be within the two red boxes in the figure below. If the EF crosses the red box on the right, the link bandwidth will decrease significantly.
4. Multi-mode fiber link bandwidth evaluation,
It is very important to evaluate the link bandwidth of multi-mode fiber when using multi-mode fiber for network distribution, because the user cannot test all VCSEL lasers and all fibers one by one. According to the specification parameters of multimode fiber and VCSEL laser, fiber link bandwidth evaluation is helpful to realize the designed link bandwidth
.5. Multimode fiber dilemma
With the increasing demand of high bandwidth rate, multi-mode fiber may be unable to meet the increasing demand of bandwidth rate in the next few years due to its own characteristics. Moreover, the manufacturing process of multi-mode fiber itself is complex and its price is high, which mainly relies on the VCSEL laser with low price. If single-mode VCSEL lasers of the same cost become widely available in the next few years, it may pose a threat to the existence of multi-mode fiber.