
There are many methods for laser classification, which can be divided into solid, gas, liquid, semiconductor, dye and optical fiber.
(1) The Solid State laser is generally small and strong, with high pulse radiation power and wide application range. Such as: Nd: YAG laser. Nd (neodymium) is a group of rare earth elements, YAG stands for yttrium aluminum garnet, and crystal structure is similar to ruby. Tm: YAG, Ho: YAG, Ho: YAG, and so on.
(2) Semiconductor lasers are small in size, light in weight, long in life and simple in structure, which are especially suitable for use in aircraft, warships, vehicles and spaceships. Semiconductor laser can change the wavelength of laser through the external electric field, magnetic field, temperature, pressure and so on, can directly convert electrical energy into laser energy, so the development is rapid.
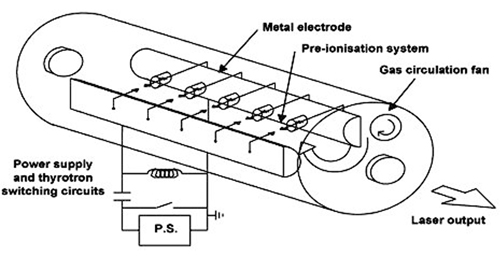
(3) Gas laser is the laser which releases current through Gas to generate coherent light. Good monochromatic and coherence, laser wavelength can be up to thousands of kinds, widely used. Gas laser has simple structure, low cost and convenient operation. Widely used in industry, agriculture, medicine, precision measurement, holographic technology and other fields. Gas laser has electric energy, thermal energy, chemical energy, light energy, nuclear energy and other excitation methods.
(4) Dye lasers, in which liquid Dye is the working substance, were invented in 1966 and are widely used in various scientific research fields. There are about 500 dyes that have been found to produce lasers. These dyes can be dissolved in alcohol, benzene, acetone, water or other solutions. They can also be contained in organic plastics in solid form, or sublimated into steam in gaseous form. So the dye laser is also called "liquid laser". The outstanding characteristic of dye laser is that the wavelength is continuously adjustable. Fuel lasers are available in a wide variety of applications, including spectroscopic, photochemical, medical, and agricultural applications, with low cost, high efficiency, and power output comparable to gas and solid state lasers.
(5) Chemical lasers: Some Chemical reactions produce enough high-energy atoms to release large energy, which can be used to produce Laser action. This is primarily a weapon application. Hydrogen fluoride lasers, for example, can provide continuous output power in the megawatt range.
(6) Free electron laser such lasers are more suitable than other types for generating high power radiation. Its working mechanism is different. It gets tens of millions of volts high-energy adjusted electron beam from the accelerator, and forms energy levels of different energy states through the periodic magnetic field, generating stimulated radiation.
(7) Excimer laser (actually one of the gas lasers) is a kind of ultraviolet gaseous laser. It is a molecule formed by a mixture of excited inert gas and another gas (inert gas or halogen). When the laser is launched to its ground state, it is called Excimer laser. Excimer laser is a low-energy laser with no thermal effect. It is a pulse laser with strong directivity, high wavelength purity and large output power. The photon energy wavelength range is 157-353 nm, and the pulse time is tens of nanoseconds. The most common wavelengths are 157 nm, 193 nm, 248 nm, 308 nm, and 351-353 nm.
(8) Fiber laser USES the gain medium (rare earth elements) in the Fiber to provide optical signal amplification. There are two kinds of fiber laser: single-end pump and double-end pump, the latter can achieve higher output power. The coherent synthesis technology under development can further extend the output power.
(9) In terms of continuity, Continuous laser and Ultrashort Pulsed laser are classified as follows: nanosecond (10e-6 SEC), picosecond (10e-9 SEC), femtosecond (10e-12 SEC), and even attosecond (10e-15 SEC). Continuous laser, longer pulse laser and Ultrashort pulse laser also act on the target surface, and the thermal effect is very different.
(10) Other types of laser has many, Raman laser Raman (laser), Metal vapor laser (Metal vapor lasers), and so on. There will be many subdivisions for different applications.
As the foundation of Industry 4.0, laser will be more and more important.
