Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) allows different data streams to be sent simultaneously over a single optical fiber network. The two key WDM technologies are Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing, CWDM and Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing, DWDM. Which solution is best suited to a given environment depends on the network and user requirements.
Both technologies are independent of protocol, meaning that any mix of data, storage, voice or video can be used on the different wavelength channels. In fiber terms, the main difference between CWDM and DWDM technologies lies in how the transmission channels are spaced along the electromagnetic spectrum.
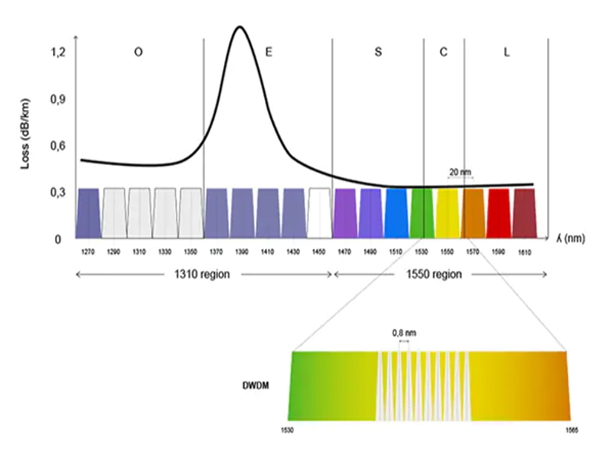
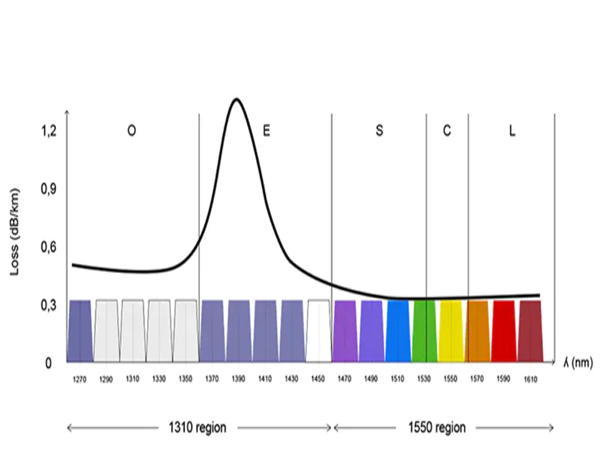
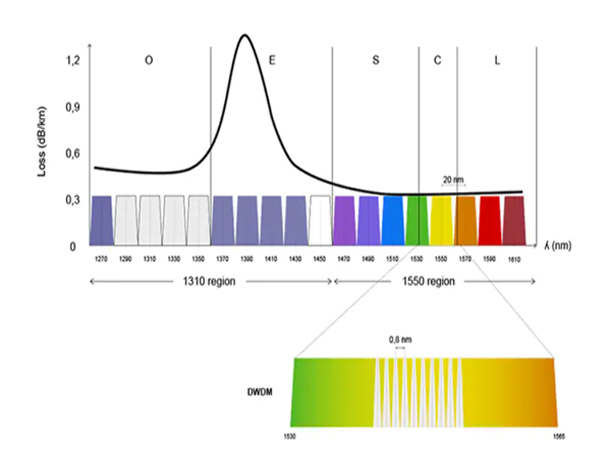
CWDM supports up to 18 wavelength channels transmitted over a dark fiber at the same time. To achieve this, the different wavelengths of each channel are 20nm apart. Two wavelength regions are most commonly associated with CWDM, 1310nm and 1550nm. The 1550nm region is more popular because it has a lower loss in the fiber (meaning the signal can travel farther).
CWDM technology offers a convenient and cost-efficient solution for shorter distances of up to 70 kilometers. For distances between 40 and 70 kilometers, CWDM tends to be limited to supporting eight channels due to a phenomenon called the water peak of the fiber (more about this further down).
DWDM supports up to 80 simultaneous wavelength channels, with each of the channels only 0.8nm apart. Unlike CWDM, DWDM connections can be amplified and can, therefore, be used for transmitting data much longer distances.
The sweet spot for CWDM is up to 10 Gigabit Ethernet and 16G Fibre Channel. And it is quite unlikely capacities with increase beyond this in the future. DWDM however, is able to handle higher speed protocols up to 100Gbps per channel making it a more suitable technology for higher speed protocols.
Traditionally CWDM components have been lower in cost making it more popular than DWDM. Now the price for both solutions is comparable. With higher speeds, more channel capacity, longer distances and passive networking, DWDM is the technology of choice for green field installations.
The figure shows how the DWDM channels fit into the wavelength spectrum compared to CWDM channels. Each CWDM channel is spaced 20nm apart from the adjacent channel. In the figure, we use colors to differentiate the 8 CWDM channels in the 1550 region. For the 1310 regions, no color schemes have been standardized.
For DWDM on the other hand, most of the DWDM channels are within the 1530 and 1550nm CWDM regions. For DWDM channels, a color scheme has not been standardized either: probably just as well because remembering all the different colors for the DWDM channels with the naked eye might also be a strain. Instead, we use a block to indicate where they are grouped.