
The emergence of DWDM is one of the most recent and important phenomena in the development of fiber optic transmission technology. This tutorial will introduce the fundamentals of DWDM technology, such as the components, optical amplifiers used in DWDM system, etc.
Components and Operation
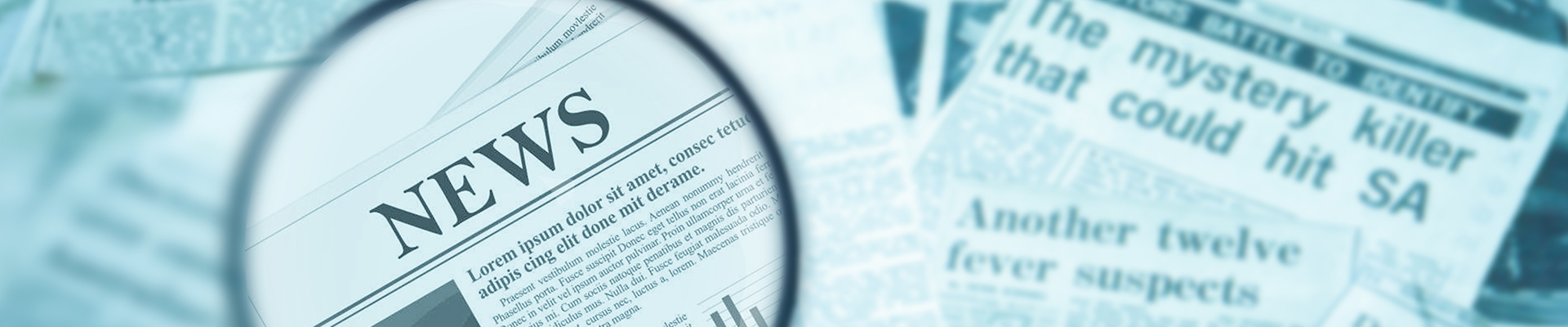
DWDM is a core technology in an optical transport network. The essential components of DWDM can be classified by their place in the system. On the transmit side, there are lasers with precise, and stable wavelengths. On the link, there is optical fiber that exhibits low loss and transmission performance in the relevant wavelength spectra, in addition to flat-gain optical amplifiers to boost the signal on longer spans. On the receive side, there are photodetectors and demultiplexers using thin film filters or diffractive elements. Besides these components, optical add/drop multiplexers and optical cross-connect components may be used.
The main job of optical fibers is to guide lightwaves with a minimum of attenuation (loss of signal). Multimode fiber and single-mode fiber are the general two categories of optical fiber in use today. Single-mode fiber has a much smaller core that allows only one mode of light at a time through the core. As a result, the fidelity of the signal is better retained over longer distances, and modal dispersion is greatly reduced. These factors attribute to a higher bandwidth capacity than multimode fibers are capable of. For its large information-carrying capacity and low intrinsic loss, single-mode fibers are preferred for longer distance and higher bandwidth applications, including DWDM.
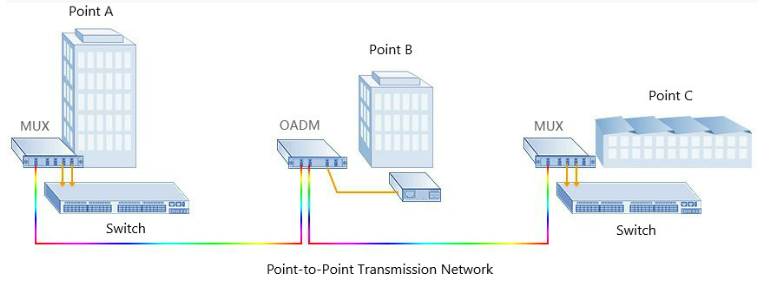
Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier (EDFA)
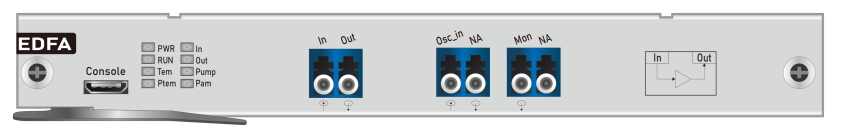
By making it possible to carry the large loads that DWDM is capable of transmitting over long distances, the EDFA was a key enabling technology. Erbium is a rare-earth element that, when excited, emits light around 1.54 micrometers—the low-loss wavelength for optical fibers used in DWDM.
Multiplexers and Demultiplexers
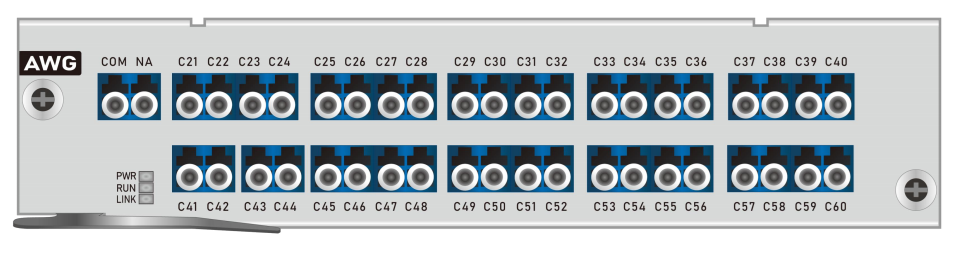
As DWDM systems send signals from several sources over a single fiber, they must include some means to combine the incoming signals. This is done with a multiplexer, which takes optical wavelengths from multiple fibers and converges them into one beam. At the receiving end, the system must be able to separate out the components of the light so that they can be discreetly detected.
Optical Add/Drop Multiplexers (OADM)
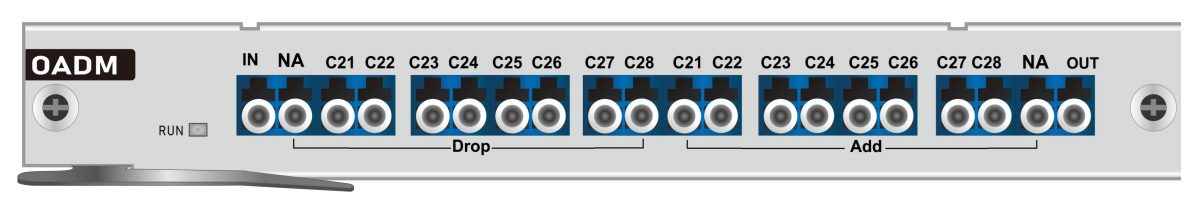
Between multiplexing and demultiplexing points in a DWDM system, there is an area in which multiple wavelengths exist. It is often desirable to be able to remove or insert one or more wavelengths at some point along this span. An optical add/drop multiplexer performs this function. Rather than combining or separating all wavelengths, the OADM can remove some while passing others on. OADM is a key part of moving toward the goal of all-optical networks.