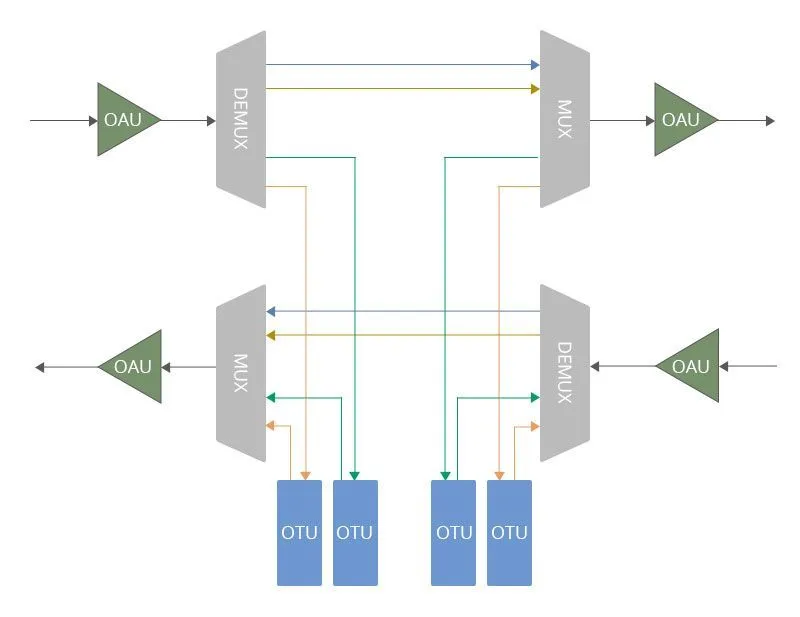
FOADM (Fixed Optical Add-Drop Multiplexer) is a type of optical add-drop multiplexer used in DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) networks that allows specific wavelengths (optical channels) to be added or dropped at a fixed point in the network. This system utilizes passive optical components like thin-film filters, fiber Bragg gratings, or arrayed waveguide gratings (AWG), which are configured during manufacturing. They are typically used in networks with stable and predictable traffic patterns, such as point-to-point or ring topologies, when the same set of wavelengths is required at specific locations.
Technical Pros and Cons:
Pros:
1: Fixed paths result in minimal signal processing, translating to lower latency.
2: Lower signal loss across the FOADM due to lower insertion loss.
3: They are typically more budget-friendly than ROADM because of their simpler design and fixed configuration.
4: Easier to design, deploy, and manage, perfect for networks with predictable traffic patterns.
Cons:
1: The fixed configuration restricts accommodating new wavelengths or services without significant hardware changes.
2: Network reconfiguration requires physical changes that are time-consuming and costly, limiting flexibility.
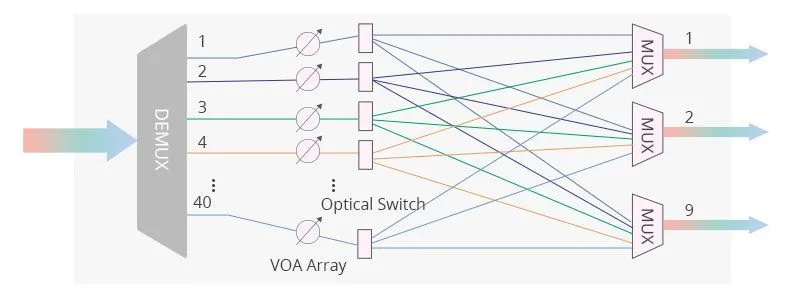
ROADM (Reconfigurable Optical Add-Drop Multiplexer) is an advanced type of optical add-drop multiplexer that allows for dynamic and remote reconfiguration of optical channels in a DWDM network. This system configuration uses tunable optical filters, wavelength selective switches (WSS), and optical cross-connects, enabling the addition, dropping, or routing of any wavelength to any port in the network without manual intervention. This configuration can be adjusted in real time through software control, enabling dynamic reconfiguration to meet changing traffic demands or network conditions. They are optimal for mesh, large metro, and core networks with variable traffic patterns that require on-the-fly reconfiguration.
Pros:
1: Enables dynamic reconfiguration for adapting to changing traffic demands and facilitates automated network management.
2: Easily scalable to accommodate new wavelengths and services as network demands grow.
Cons:
1: The dynamic nature of ROADMs requires advanced management systems and increases potential failure points.
2: The advanced components and the need for real-time control systems make ROADMs more expensive to deploy and maintain than FOADMs due to their advanced skills.
The best choice between FOADM and ROADM depends on your network’s specific needs, whether you prioritize the simplicity and cost that FOADM can promote or require the adaptability and growth potential that ROADMs provide.
If you want to buy this DWDM/EDFA/DCM/OLP/OADM/MUX/DEMUX/SOA/ROMAN/OTDR/WSS/OTU/MUXPONDER/TRANSPONDER product, welcome to contact HTF, HTF can help you expand the network capacity by DWDM solution.
HTF can help you design coherent 400G/200G/100G DWDM/OTN solution, DWDM Single lamda support 100G/200G/400G Dual fiber/Single fiber Ultra long distance transmission. Expand your network capacity and DCI network easily.