Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) is an advanced optical communication technology that allows multiple optical signals to be transmitted simultaneously on a single optical fiber, significantly increasing the capacity and efficiency of optical communication. The core components of a DWDM system include the optical wavelength converter, wavelength division multiplexer, optical amplifier, and dispersion compensator.
Optical Wavelength Converter
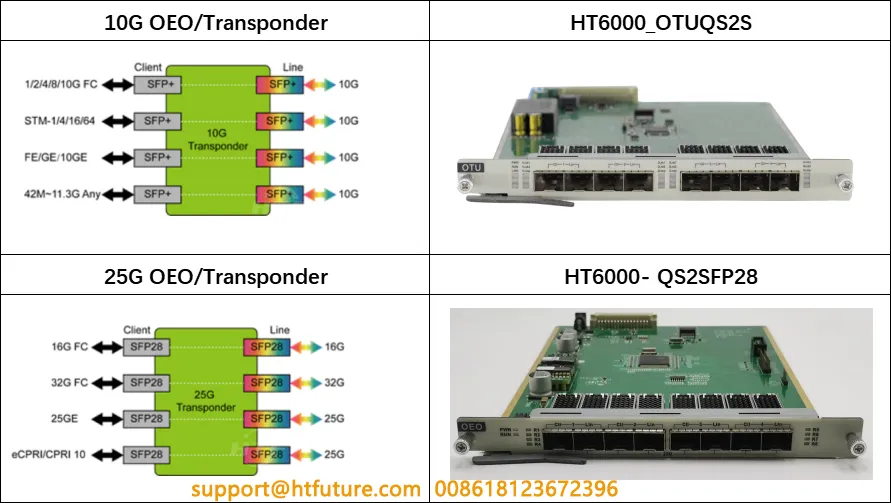
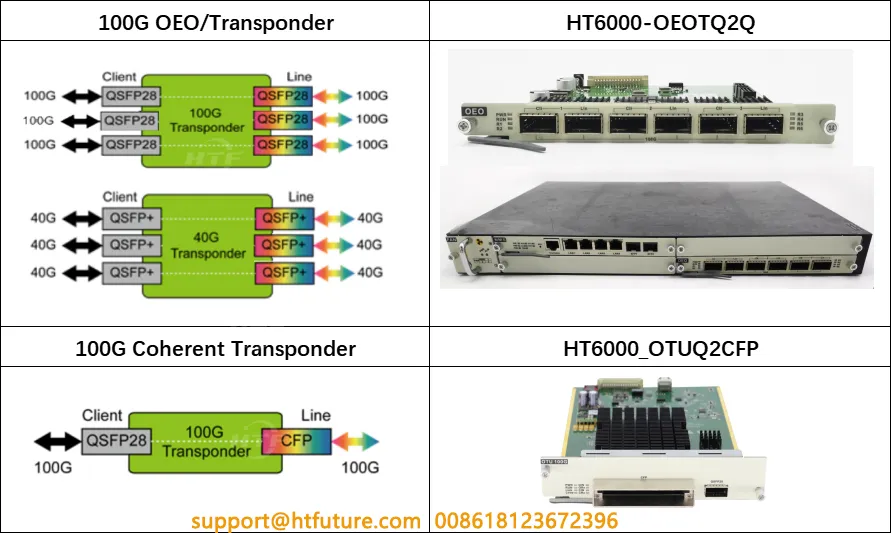
The Optical Wavelength Converter is one of the key components in a DWDM system. Its main function is to convert optical signals of different wavelengths into specific wavelengths required by the system, allowing these signals to be transmitted on the same optical fiber. The wavelength conversion process usually involves optical-electrical conversion, where the input optical signal is converted to an electrical signal and then to an output optical signal of a different wavelength.
Wavelength conversion technology helps to resolve wavelength conflicts, ensuring that each signal can be transmitted at the correct wavelength. This is crucial for the network’s dynamism and flexibility, as it allows for dynamic allocation and adjustment of wavelength resources, thereby improving network utilization efficiency and service quality.
Wavelength Division Multiplexer
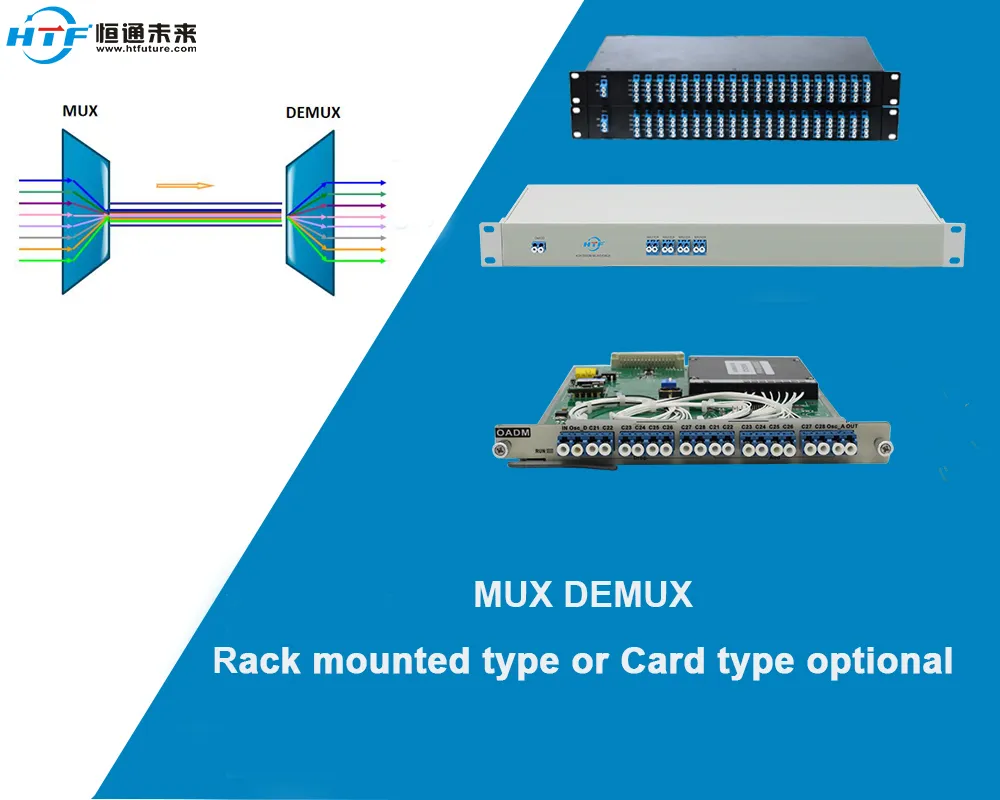
The Wavelength Division Multiplexer (WDM MUX) is a device that combines multiple optical signals of different wavelengths into a single optical fiber. It is the core component that enables high-capacity transmission in DWDM systems. Using technologies like diffraction gratings or arrayed waveguide gratings, the wavelength division multiplexer accurately combines optical signals of different wavelengths and separates them at the receiving end through a wavelength demultiplexer.
In practical applications, the wavelength division multiplexer can effectively utilize the bandwidth of the optical fiber, significantly increasing transmission capacity. For example, a DWDM system with 80 channels can achieve the transmission of up to 80 different wavelength signals on a single fiber, with each channel’s transmission rate reaching up to 100Gbps or higher, resulting in a total transmission capacity of several Tbps.
Optical Amplifier
The Optical Amplifier is used in DWDM systems to compensate for the attenuation of optical signals during transmission. Commonly used optical amplifiers include Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifiers (EDFA) and Raman Amplifiers. EDFA is the most commonly used type, especially suitable for amplifying optical signals in the C-band (1530-1565nm).
Optical amplifiers can directly amplify optical signals without converting them to electrical signals, greatly simplifying system design and improving transmission efficiency. In long-distance optical fiber transmission, optical amplifiers are spaced along the transmission path to ensure that the optical signal strength remains sufficiently high, avoiding severe signal attenuation and distortion.
Dispersion Compensator
The Dispersion Compensator is used to compensate for dispersion effects in optical fibers. Dispersion refers to the phenomenon where optical signals of different wavelengths travel at different speeds in the fiber, causing signal pulse broadening and distortion, thus affecting communication quality. In DWDM systems, due to high transmission rates and dense wavelengths, dispersion effects are more pronounced and must be effectively compensated.
Common dispersion compensation technologies include Dispersion-Compensating Fiber (DCF) and Dispersion Compensation Modules (DCM). DCF introduces reverse dispersion characteristics into the fiber to compensate for signal dispersion, while DCM achieves dispersion compensation through optical filters and other technologies. The use of dispersion compensators can significantly improve the transmission performance of the system, ensuring high-quality signal transmission.
The composition of DWDM systems involves multiple key components, each playing an important role in the system. The optical wavelength converter ensures that signals are transmitted at the correct wavelengths, the wavelength division multiplexer achieves the merging and separation of multi-wavelength signals, the optical amplifier compensates for signal attenuation during transmission, and the dispersion compensator addresses dispersion issues during transmission. Through the coordinated operation of these components, DWDM systems can achieve high-capacity, long-distance, and high-quality optical communication, providing strong support for modern communication networks.