What is CWDM and DWDM?
Before diving into “Universal Platform Design,” let’s clarify what CWDM and DWDM are:
| Technology | Full Name | Meaning | Key Features |
| CWDM | Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing | Coarse WDM | Wide channel spacing, low cost, suitable for short distances |
| DWDM | Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing | Dense WDM | Narrow channel spacing, high capacity, ideal for long-haul, high-speed transmission |
Simple Analogy:
CWDM: Like a wide-lane road—fewer cars, lower cost, but limited speed.
DWDM: Like a multi-lane highway—narrow lanes, but more cars, faster, and longer distances.
Both are optical fiber multiplexing technologies, using different wavelengths (colors) of light to transmit massive data over a single fiber—turning one fiber into a multi-lane data highway.
What is CWDM/DWDM Universal Platform Design?
1. Definition
CWDM/DWDM Universal Platform Design refers to a highly compatible and flexible optical transmission system architecture that supports both CWDM and DWDM technologies. It enables multi-service access and unified management, optimizing network resource utilization while reducing construction and operational costs.
2. Simple Explanation
Imagine designing a “smart highway”:
It can handle wide lanes (CWDM) for slower traffic,
And narrow lanes (DWDM) for high-speed traffic,
Plus, it can dynamically adjust lanes and speeds based on traffic demand.
This is the core concept of a CWDM/DWDM Universal Platform—a single platform to handle diverse optical transmission needs.
Design Philosophy and Key Elements of CWDM/DWDM Universal Platform
1. Design Philosophy
Unified Architecture, Flexible Deployment: One hardware platform supporting CWDM, DWDM, or hybrid networking.
Modular Design: Plug-and-play modules for easy expansion and maintenance.
Service Agnostic: Transparent transmission for multiple services (Ethernet, SDH, OTN, SAN, etc.).
Cost Efficiency: Maximize ROI by balancing bandwidth needs with investment and operational costs.
2. Key Design Elements
| Element | Description |
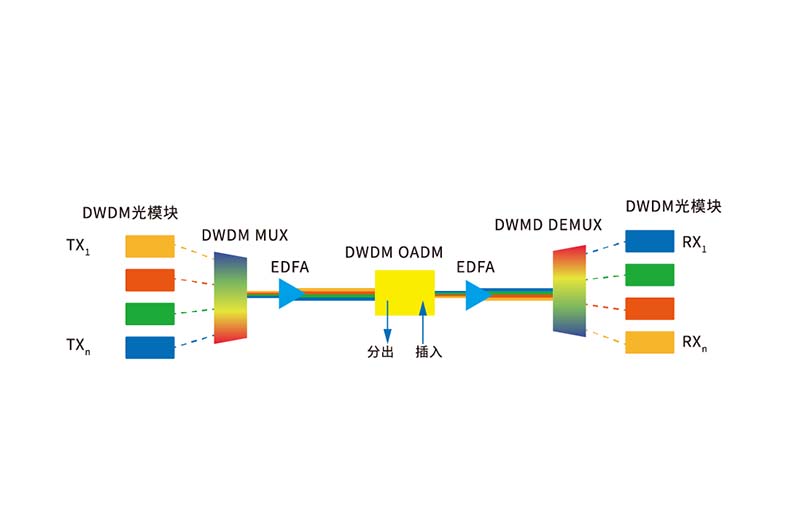
| Multiplexers/Demultiplexers (Mux/Demux) | Compatible with both CWDM and DWDM wavelengths |
| Optical Amplifiers (EDFA) | Essential for long-distance DWDM, configurable in a universal setup |
| OADM Modules | Optical Add-Drop Multiplexers for flexible wavelength access |
| Network Management System | Centralized intelligent management for CWDM and DWDM devices |
| Tunable Lasers | Dynamic wavelength adjustment, reducing spare parts inventory |
| Wavelength Conversion | Enables seamless CWDM and DWDM hybrid deployments |
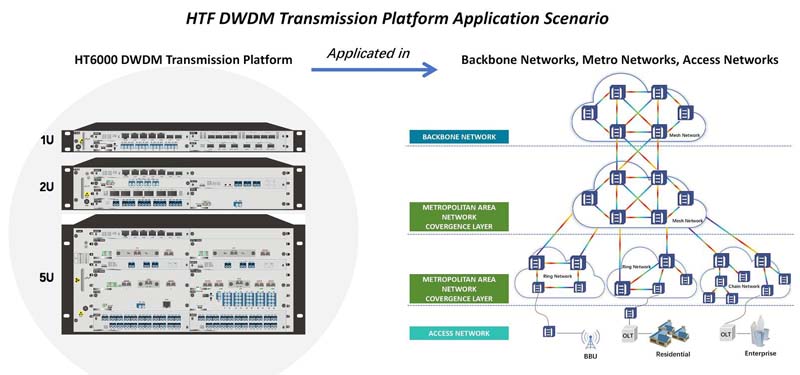
Application Scenarios for CWDM/DWDM Universal Platform
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
Start with CWDM for basic bandwidth, smoothly upgrade to DWDM as demands grow.
Data Center Interconnection (DCI)
Flexible and efficient optical transmission between data centers.
Carrier Backbone and Access Networks
Optimize deployment by using CWDM, DWDM, or hybrid solutions based on traffic density.
Enterprise Private Networks
Provide scalable, secure, and cost-effective multi-service optical transport for large enterprises.
Advantages of CWDM/DWDM Universal Platform
| Advantage | Description |
| High Flexibility | Dynamically adjust CWDM or DWDM configurations as needed |
| Cost Reduction | Minimize equipment redundancy, unify operations, optimize investment |
| Simplified Management | Centralized monitoring and control through a unified system |
| Strong Scalability | Easy capacity expansion to meet future bandwidth growth |
| Multi-Service Support | Transparent transport of various service types |
Hybrid CWDM and DWDM Network Example
Scenario:
A company connects headquarters to branches with limited fiber resources. Initially, CWDM with 8 wavelengths meets basic needs.
As traffic increases, certain channels are subdivided using DWDM for high-density transmission.
The universal platform only requires adding DWDM modules—no need for rewiring or major equipment changes.
The CWDM/DWDM Universal Platform Design represents a key trend in modern optical transmission networks. It eliminates the limitations of single-technology systems, achieving:
Flexible service deployment,
Optimized cost efficiency,
A solid foundation for sustainable network evolution.
For telecom operators, enterprises, and data centers, adopting such a platform not only addresses current demands but also ensures readiness for the next decade of network growth.