In today’s world, swept by the wave of digitalization, optical fiber communication technology, with its unparalleled high-speed transmission capabilities and stability, is propelling human society to new heights in the information age. From the widespread deployment of 5G networks to the booming development of cloud computing and the Internet of Things (IoT), the explosive growth of data traffic poses unprecedented challenges to communication networks.
Against this backdrop, the Optical Transport Network (OTN), as a core technology in modern optical fiber communication, stands out with its exceptional performance and flexibility, emerging as a critical force in connecting the world and driving technological innovation.
Basic Concepts and Working Principles of OTN
OTN is a next-generation optical transmission technology based on the ITU-T G.709 standard. It maximizes the synergy between the optical and electrical domains, designed to efficiently carry and transmit diverse types of service data. The core structure of OTN includes the Optical Channel Transport Unit (OTU), Optical Channel Data Unit (ODU), and Optical Channel Payload Unit (OPU).
This hierarchical design endows OTN with powerful capabilities: it can encapsulate various service signals—such as Ethernet, SDH, and storage networks—into a unified frame structure, enabling parallel transmission of multiple signals over a single fiber through Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) technology.
Metaphorically, OTN is like a vast highway network, where diverse service signals are akin to vehicles, systematically loaded and transported to their destinations. Its built-in Forward Error Correction (FEC) mechanism serves as a “safety barrier,” significantly reducing bit error rates during transmission through error-correcting algorithms, ensuring data remains clear and reliable over long distances.
This synergy between optical and electrical operations not only provides OTN with ultra-high transmission efficiency but also equips it with robust network management and protection capabilities, making it a cornerstone of optical fiber communication.
Key Roles of OTN in Optical Fiber Communication
OTN holds an irreplaceable position in the optical fiber communication ecosystem, serving not only as a bridge between the access and core layers but also as an engine driving leaps in network performance. Its roles can be analyzed from several key perspectives:
1.Multi-Service Carrying Capacity
In modern communication networks, service types are diverse, ranging from traditional TDM signals to emerging Ethernet and video streams. OTN can transparently carry them all. Through a unified encapsulation format, it integrates signals from different protocols into high-speed optical channels.
For example, in 5G fronthaul networks, OTN efficiently transmits base station data; in Data Center Interconnect (DCI) scenarios, it supports large-scale data exchanges between cloud service providers. This multi-service compatibility makes OTN an ideal choice for diverse needs.
2.Efficient Bandwidth Utilization
Combined with Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) technology, OTN pushes fiber transmission capacity to its limits. Through multi-wavelength multiplexing, it can carry dozens or even hundreds of high-speed channels on a single fiber, far surpassing traditional technologies in bandwidth utilization. Additionally, OTN supports flexible bandwidth allocation, dynamically adjusting resources based on service demands to ensure optimal use of every bit of data.
3.Long-Distance Transmission Assurance
Long-distance transmission is a typical requirement in optical fiber communication, and OTN’s FEC technology significantly enhances signal quality. For instance, in transcontinental submarine cable systems, FEC can reduce bit error rates to below 10^-15, ensuring data integrity over thousands of kilometers. This capability extends the reach of optical signals, reduces the need for relay equipment, and lowers network construction costs.
4.Network Management and Reliability
OTN’s built-in Operations, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM) functions act as an “intelligent steward” for the network. It monitors performance in real-time, quickly detects faults, and triggers protection switching when necessary.
For example, if a fiber link fails, OTN can swiftly restore services via preconfigured backup paths, ensuring network availability exceeds 99.999%. This high reliability provides operators and enterprises with robust communication guarantees.
In summary, OTN’s multi-service carrying capacity, efficient transmission, and reliable management make it an indispensable pillar of optical fiber communication networks, supporting everything from urban backbone networks to global interconnectivity.
Technical Advantages of OTN
OTN’s prominence in optical fiber communication stems from its unique technical advantages, akin to a “multifunctional Swiss army knife,” delivering comprehensive improvements to network construction and operations:
1.Standardization and Compatibility
Based on the G.709 standard, OTN defines a unified frame structure and protocol, ensuring seamless interoperability between equipment from different vendors. Compared to traditional SDH/SONET technologies, OTN supports higher rates (e.g., 100G, 400G, and even 800G) and offers more flexible service scheduling. This standardized design reduces network construction complexity and enhances global communication collaboration.
2.Flexibility and Scalability
OTN’s bandwidth scalability is impressive, spanning from 1Gbps to over 1Tbps, enabling it to effortlessly handle future traffic surges. For instance, with the maturity of 800G technology, OTN is being deployed in core networks, laying the foundation for the next-generation internet. Its modular design also allows operators to upgrade equipment incrementally, balancing performance and cost.
3.Optical-Electrical Synergy Optimization
OTN seamlessly integrates the optical layer (WDM) with the electrical layer (cross-connect), optimizing resources end-to-end. At the optical layer, it leverages multi-wavelength technology to expand capacity; at the electrical layer, it uses digital signal processing for precise scheduling. This synergy ensures stable network operation under high loads, such as in DCI, where OTN optimizes bandwidth allocation and boosts transmission efficiency.
4.Low Latency and High Reliability
For latency-sensitive applications like 5G, OTN minimizes transmission delays through optimized frame structures and rapid protection mechanisms. It also supports 1+1 or 1:N backup schemes, ensuring swift switching during faults to meet the high-reliability needs of critical services. This is particularly valuable in scenarios like financial trading and telemedicine.
These technical advantages collectively form OTN’s competitive edge, securing its unshakable position in optical fiber communication.
OTN Application Scenarios and Future Outlook
OTN’s applications are vast, spanning nearly every facet of modern communication networks:
– Carrier Backbone Networks: In national or provincial backbone networks, OTN supports high-speed inter-city data transmission, serving as the internet’s “main artery.”
– Enterprise Private Lines: It provides highly reliable, low-latency dedicated services for industries like finance and healthcare, ensuring business continuity.
– Data Center Interconnect: In the cloud computing era, OTN enables efficient channels for massive data exchanges between data centers.
– 5G Transport Networks: From fronthaul to backhaul, OTN meets 5G base stations’ demands for high bandwidth and low latency, advancing mobile communication to new heights.
Looking ahead, as global data traffic continues to grow, OTN will encounter new development opportunities. Achieving rates above 1Tbps and integrating with quantum communication technologies will further enhance its transmission capabilities. Meanwhile, intelligent network management (e.g., SDN integration with OTN) will make it more flexible and efficient, adapting to diverse scenarios. OTN is not only the cornerstone of current communication networks but also a bridge to the future.
With its multi-service carrying capacity, efficient bandwidth utilization, and robust network management, OTN plays a pivotal role in optical fiber communication. Its technical advantages—standardization, flexibility, and optical-electrical synergy—provide a solid foundation for high performance and reliability. Driven by 5G, cloud computing, and global interconnectivity, OTN is leading communication technology innovation with unstoppable momentum, unlocking infinite possibilities for the digital era.
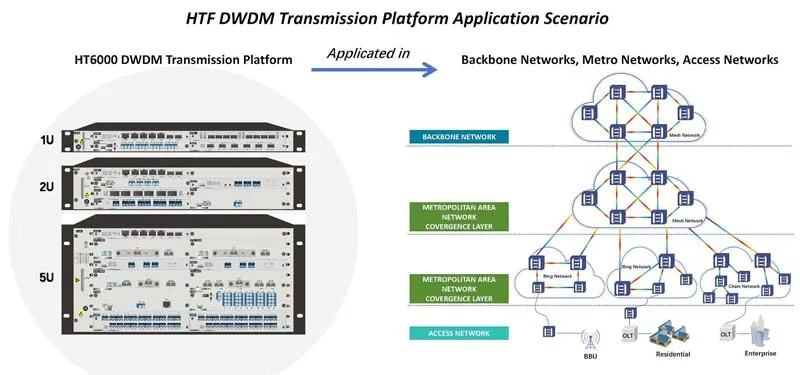
Notably, in practical applications of OTN technology, the HTF HT6000 has set a new industry benchmark. Launched by HTF as a compact, high-capacity, cost-effective OTN optical transmission system, the HTF HT6000 adopts a CWDM/DWDM universal platform design, supporting transparent multi-service transmission with flexible networking and access capabilities.
Suitable for national backbone networks, provincial backbone networks, metropolitan backbone networks, and other core networks, it meets large-capacity node demands exceeding 1.6T, making it one of the most cost-effective transmission platforms in the industry. For IDC and ISP operators building large-scale WDM transmission expansion solutions, the HTF HT6000 exemplifies OTN’s critical value in modern communication with its outstanding performance and affordability, helping propel global networks toward a more efficient and intelligent future.