Dense wavelength-division multiplexing (DWDM) is an optical transmission technology that uses multiple wavelengths of light to combine several data streams onto a single optical fiber. DWDM is a subset of wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) that typically uses the spectrum band within 1530nm and 1625nm, or more commonly the C-band and L-band, to input 40, 88, 96 or even 160 wavelengths, or channels, onto a single strand of fiber optic cable.
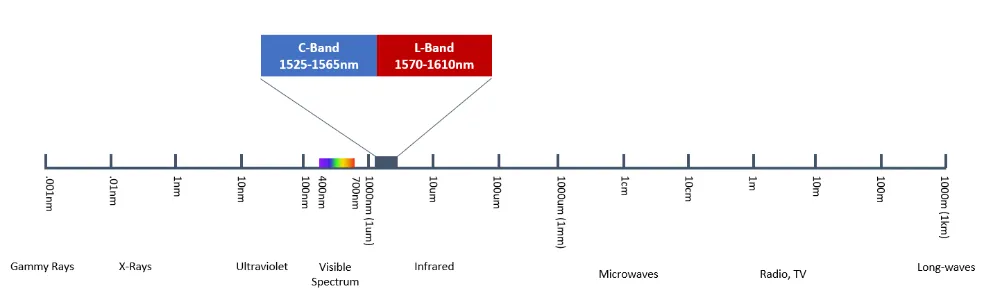
DWDM got its name from using tighter wavelength spacing (dense) to fit more channels, with each channel being only about 0.8nm wide. This is opposed to its WDM sibling, CWDM, where it uses a wider range of frequencies, with each channel spread farther apart. With a CWDM channel being 20nm wide, the high number of channels available to DWDM means it can cram much more data into the cable.
How does DWDM Work?
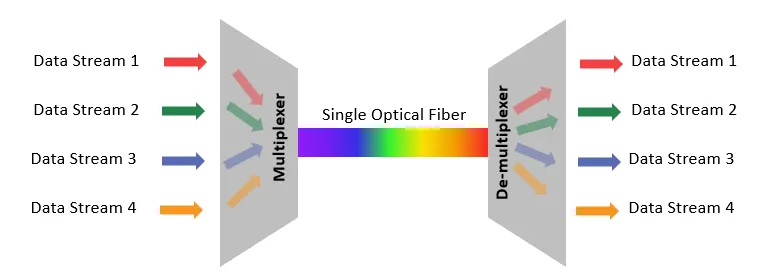
To explain how DWDM works, we first need to explain how the WDM works. Wavelength-division multiplexing, or WDM, uses a multiplexer to join several different data streams and convert them into wavelengths of light before transmitting it over the fiber optic cable, which is then de-multiplexed at its receiving end and split back into its respective streams of data.
Being a dense form of WDM, DWDM uses the same multiplexer to de-multiplexer transmission method, except that it can fit much more channels. To put that into perspective, if each channel carries 100Gbps of data, then at 160 channels per fiber cable, DWDM can essentially have a capacity of 1.6Tbps of data per fiber cable.
What are the Benefits of DWDM?
The major benefit of using DWDM technology is that it can transmit a large amount of data over a very long distance, which makes it very suitable for long-haul transmission. It can also be used with existing fiber optic cables with the means of increasing their data capacity as optical technology improves.
DWDM technology is useful when data needs to be sent across several states or even across oceans. Where it is much cheaper to install a DWDM system rather than laying down hundreds or thousands of kilometers of new fiber.
Another benefit DWDM technology has for data transmission is that DWDM is protocol and bitrate independent, because as data flows through each wavelength, the channels do not interfere with one another. This means DWDM can carry different types of traffic such as voice, video, and text over a single fiber optic cable, which is very beneficial to service providers who offer multiple services to their customers. This non-interference also helps to maintain the integrity of data and enable the separation of users and other types of partitioning applications.