1. Working Principle
ROADM is an upgraded version of OADM, offering greater flexibility and configurability to dynamically adjust wavelength routing. In addition to adding and dropping wavelength signals like OADM, ROADM can reconfigure network paths as needed, enabling arbitrary wavelength routing.
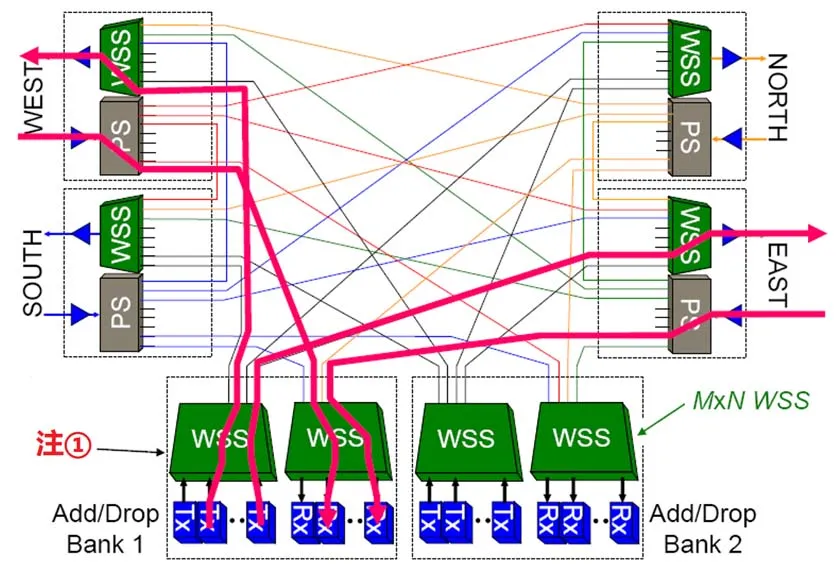
Dynamic Wavelength Routing: ROADM achieves dynamic routing through Wavelength Selective Switches (WSS) and programmable optical switches, allowing signal paths in the network to be adjusted based on traffic demands.
Wavelength Insertion and Deletion: Similar to OADM, ROADM supports selective addition and removal of wavelengths. However, its advantage lies in its ability to enable dynamic wavelength scheduling across the entire network, making wavelength management more efficient.
No Electrical Conversion: ROADM typically processes signals entirely optically, avoiding electrical conversions, which significantly reduces latency and power consumption.
2. Application Scenarios
Core and Long-Haul Optical Networks: ROADM is widely used in backbone networks requiring high levels of dynamism and flexibility. It effectively supports large-scale, high-speed optical networks.
Example: Dynamic wavelength routing in backbone networks. In optical fiber backbone networks that need to quickly respond to traffic fluctuations, ROADM devices use dynamic routing to adjust signal paths based on traffic demands. For instance, in China’s transnational optical fiber backbone networks, ROADM enables dynamic wavelength scheduling between countries and cities, effectively handling traffic surges during peak periods.
Automated Optical Networks: ROADM enables automated configuration and routing within networks, significantly enhancing intelligent network management, which aligns with future network development needs.
ROADM in WDM Systems
ROADM plays a critical role in WDM systems by supporting fully dynamic wavelength configuration. This enables optical networks to adapt more flexibly and efficiently to varying traffic demands. In multi-wavelength systems, ROADM dynamically schedules optical wavelengths as needed, improving wavelength utilization and reducing congestion in optical networks.
| Functionality | OXC | OADM | ROADM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main Functions | Wave length conversion | Wave insertion and drop | Wave insertion, drop, and switching |
| Flexibility | High, suitable for long-haul, cross-connect | Medium, suitable for metropolitan access | High, suitable for metro and core network |
| Application Scenarios | Long-haul optical fiber links, cross-connect | Metro access, ring networks, regional transportation | Metro core networks, backbone transport, flexible regional connections |
| Technical Complexity | High, using tunable lasers, wavelength converters | Medium, using wavelength selective components | High, using wavelength selective switches, tunable transponders |
| Capacity | High, supports many wavelengths | Medium, supports fewer wavelengths | High, supports a large number of wavelengths |
| Adaptability | Supports wavelength conversion and exchange | Supports wavelength insertion and drop | Supports wavelength insertion, drop, and switching according to demands |
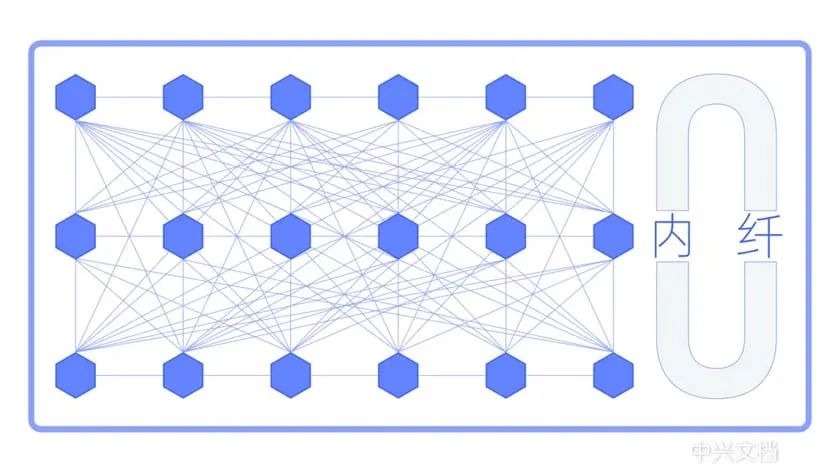
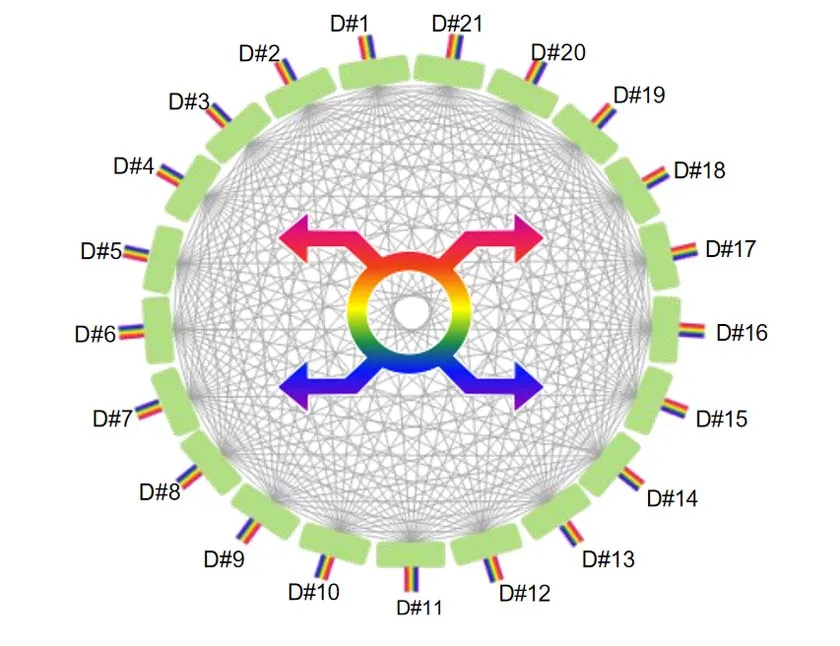
Core Value of OXC: Simplified Deployment, Accelerated Expansion, and Enhanced Flexibility in Optical Communication Networks
1.Bid farewell to the tedious manual fiber connections and achieve automated configuration.
2.High-integration architecture makes rapid expansion no longer a challenge.
3.Reduce activation time from days to hours, improving network responsiveness.
4.Optimize operational efficiency and lower maintenance costs.
5.A key enabler for intelligent optical networks.
OXC technology addresses the complexity, expansion challenges, and maintenance bottlenecks of traditional optical switching systems. Through highly integrated optical backplanes and modular architectures, it enables faster deployment, more flexible scaling, and more efficient operation. Its capabilities of “day-level” activation and “hour-level” expansion not only improve network responsiveness but also lay a solid foundation for the future of intelligent optical networks.